LODF Screening
This tool is found on the Tools ribbon tab in the Run Mode ribbon group under Sensitivities > LODF Screening.
The goal of this tool is to create pairs of contingencies that are significant without actually solving all of the contingencies. The methods are based on the technical paper - C. Matthew Davis and Thomas J. Overbye, "Multiple Element Screening," IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 1294-1301, Aug. 2011.
The Lines to Process (Outage) and Lines to Monitor options determine how the LODFs will be calculated. For each line that is processed as an outage, the impact of that outage (LODF) will be determined for each of the monitored lines. Optionally, LCDFs will be calculated for lines that are open. For brevity, the term outage will mean any line that is being processed regardless of its status.
Lines to Process (Outage)
This option determines which lines will be considered as outages when calculating LODFs.
All ac Lines
All branches in the case will be taken as outages.
Defined Contingencies
Branch elements contained in contingencies of action type OPEN or CLOSE will be taken as single outages.
Limit Monitoring Settings
Only branches meeting the limit monitoring settings options for monitoring will be taken as outages.
Use Area/Zone/Owner Filter
Only branches meeting the Area/Zone/Owner filter will be taken as outages.
Use Selected
Only branches where the Selected field is YES will be taken as outages.
Meets Filter
Only branches that meet the specified advanced filter will be taken as outages.
Lines to Monitor
This option determines which lines will be considered as lines to monitor when calculating LODFs. Only branches that are online are monitored.
Same as Lines to Process
The same set of lines that will be treated as outages will also be monitored.
All ac Lines
All branches in the case will be monitored.
Limit Monitoring Settings
Only branches meeting the limit monitoring settings options for monitoring will be monitored.
Use Area/Zone/Owner Filter
Only branches meeting the Area/Zone/Owner filter will be monitored.
Use Selected
Only branches where the Selected field is YES will be monitored.
Meets Filter
Only branches that meet the specified advanced filter will be monitored.
Options
The following options will determine how the resulting contingency combinations are determined.
Include Phase Shifters
Checking this option will assume that phase shifters are allowed to operate to maintain their desired flow. This results in no change in flow on a phase shifter due to a line outage, i.e. LODF = 0.
Include Open Lines
Checking this option will include lines that are open as lines to process. This will result in LCDF values being calculated on any open lines.
LODF Threshold
Check this option to use the Impact Tracking Structure (ITS) screening method. The threshold value specifies what is considered a significant LODF during this screening method. The minimum value that can be specified is 1%.
The ITS screening method uses LODFs to determine significant single contingencies for monitored elements based on the magnitude of the LODF. Pairs of significant contingencies are created from single contingencies that impact a single monitored line.
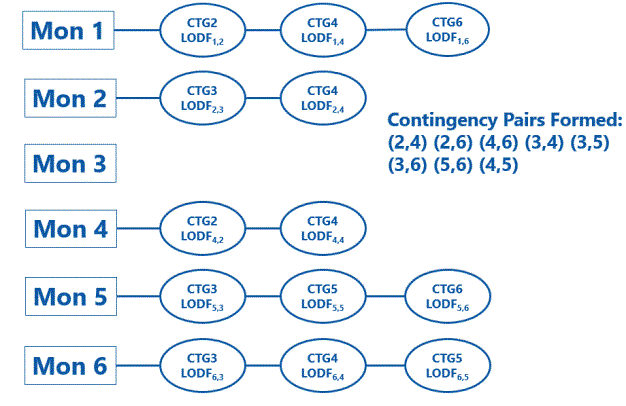
The following example shows how contingency pairs are formed. LODFs are calculated for each of the monitored lines for each of the outages. The monitored lines are indicated by the rectangles on the left. A significant outage is one for which the absolute value of its LODF is greater than the specified LODF Threshold for that monitored line. Each of the CTG bubbles next to a monitored line indicates a line that was processed and results in a significant LODF for that monitored line. New contingency pairs are formed by combining pairs of significant contingencies for each monitored line.
Overload Threshold
Check this option to use the Outage Tracking Structure (OTS) screening method. The range of values specifies the minimum and maximum range for percent loading of a monitored line. Only outages that cause loadings on the monitored lines within this range are considered significant for a particular monitored line. LODFs and LCDFs are used to determine the loadings on monitored lines. Pairs of significant contingencies are created from significant single contingencies that impact any monitored line and all other outages being studied.
The following example shows how contingency pairs are formed. LODFs are calculated for each of the monitored lines for each of the outages. The monitored lines are indicated by the rectangles on the left. The LODFs are used to calculate the flow on the monitored line during the outage. A significant outage is one in which the loading on the monitored line is within the specified percent loading range. Each of the CTG bubbles next to a monitored line indicates a significant outage. New contingency pairs are formed by combining pairs of significant outages for any monitored line and all other outages being studied. In this example CTG 1 through 6 are studied outages and are combined with each of the significant outages that cause loadings on the monitored lines.

To calculate the line loadings, Limit Monitoring Settings are used to determine the contingency limit for each monitored line. If a monitored line is part of a multi-section line, the most limiting contingency limit is used for all segments.
To calculate the line flows, contingency DC Method Options that determine whether to calculate based on amps and how to model reactive power are used.
Calculate LODFs
Click this button to do the calculations. The progress bar will show the relative amount of time left in the calculation and the message box will indicating any errors.
File Information
The File Location will specify a directory in which an aux file containing the contingency definitions will be saved. Clicking the Browse button will open a dialog from which the file location can be selected. A file will be saved at this location with LODFScreening.aux as the name. Click the Save to File button to actually save the file. Contingencies can only be created by saving them to file.
When naming the contingencies, the Auto Insert Contingencies options for naming contingencies will be used by default. If the Use Available Contingency Names for New Contingency Names option is checked and an outage is part of an existing contingency, the new contingency name will incorporate the name of the existing contingency.
Summary Information
This section is for information only. How many lines to process and monitor are shown. Number of Combinations without Screening indicates how many pairs of contingencies would be created if simply combining all studied outages in pairs. Number of CTG Combinations indicates how many pairs are determined based on the selected screening options.
Assign Summary to Branch Custom Fields
Information in the Summary Table only exists while the LODF Screening dialog is open and cannot be accessed through auxiliary files or script commands. To make this information accessible, it can be saved to custom floating point or custom string fields with Branch records. The branch record to which the information is stored corresponds to the Contingency Line specified in the summary table. Use each dropdown to select the custom field to which the corresponding value will be assigned. For Highest LODF Value and Highest Overload Value, custom floating point fields can be selected. For Original CTG Name, Highest LODF Line and Highest Overload Line, custom string fields can be selected. Click the Populate button to actually assign the values once the fields have been selected.
Summary Table
This table provides information for the highest LODF and highest loading for monitored lines under each outage, Contingency Line, that is studied for which a monitored line has a significant LODF or loading. If using the LODF Threshold option, the Highest LODF field shows the absolute value of the highest LODF greater than the LODF Threshold, and Highest LODF Line indicates the monitored line for which this LODF is calculated. If using the Overload Threshold option, the Highest Overload field shows the highest percent loading between the specified range, and the Highest Overload Line indicates the monitored line with this loading.
The Original Contingency Name field indicates the contingency from which the single line studied as Contingency Line originated. This is only populated if using the Lines to Process (Outage) option of Defined Contingencies.
The key fields used for identifying objects in this table will change depending on the Key Fields to Use in Subdata Sections option specified with Case Information Display Options.