Contingency Iterated Linear Analysis
Linear analysis of the impact of contingencies is done by calculating sensitivities (LODFs and power injection sensitivities) based on a solved power flow Jacobian. No contingency actions are actually implemented and the system state does not change. This poses a limitation to accurately modeling the impact of conditional actions within a contingency when all conditions are evaluated in the contingency reference state instead of being evaluated following the implementation of other actions. To model conditional actions more accurately, an iterative approach to the linear analysis can be taken. Instead of doing a single calculation with all conditions modeled in the contingency reference state where TOPOLOGYCHECK and POSTCHECK actions are treated as CHECK actions, contingencies are processed in the order of a full ac solution, but instead of solving the power flow the linear impact of all actions that can be implemented is determined. This process will most likely be slower than the non-iterative linear calculation, but will yield the benefits of a more accurate solution when that is required from the linear calculations, such as with ATC calculations.
Using the Iterated Linear Analysis Method
To use the iterated linear analysis method, the contingency Calculation Method must be set to one of the Linearized options and the Iterate on Action Status option must be selected. The power flow solution options must also be set for ac power flow.
Determining if Iterated Process is Needed
Even though the appropriate settings are selected to use the iterated linear analysis method, it might not be necessary to use it. To save on calculation time, Simulator will only use the process when necessary. At the beginning of each contingency process that is set to use the iterated linear process, a pre-processing is done to determine if it is necessary. It will only be necessary if a field needs to be evaluated in some contingency state other than the reference state and it is a handled field. The Which Fields are Handled section describes how you can determine these. It will be necessary if any of the following are found:
- TOPOLOGYCHECK action using a Model Criteria (Model Condition, Model Filter, and Model Expression are checked) with a handled field
- POSTCHECK action using a Model Criteria (Model Condition, Model Filter, and Model Expression are checked) with a handled field
- Contingency action specifying the Amount of change by either a Model Field or Model Expression and the Evaluate in Reference State option is set to NO
Which Fields are Handled
Because linear contingency analysis does not actually change the system state, only fields that are specifically defined to be evaluated during a linear contingency state will be handled correctly. All other fields will ALWAYS be evaluated in the contingency reference state. Determining which fields should be handled will be a learning process of checking conditional actions and adding fields as necessary. We will require user input on doing this.
A tool has been added to provide a summary of fields that are handled and which ones are in use by conditional checks or contingency actions that are not handled. The local menu of the Contingencies table contains the Verify Contingencies for Iterated Linear Analysis tool that will process the current list of contingencies, Remedial Actions, and Global Actions to determine which fields are and are not handled. A user-specified text file will store the results.
The file will look something like the following. If you have any fields in the NOT handled section, please contact PowerWorld for assistance.
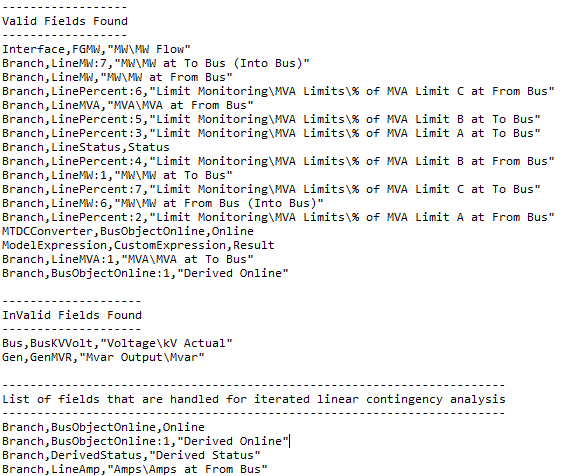
Calculating Flows During Iterated Method
- MW flows are determined from the contingency reference state MW plus the change in MW flow from the contingency determined by using LODF calculations.
- MVA flows are calculated based on the MW flows and the Reactive Power Model chosen.
- The Reactive Power Model comes from the contingency options during contingency analysis
- The Reactive Power Model comes from the ATC options during ATC analysis but the flows are calculated based on the contingency methodology.
- Amps determined from MVA and contingency reference state voltages