Transmission Line Parameter Calculator
The transmission line parameter calculator is a tool designated to compute characteristic line parameters give the type of the conductor and the configuration of a three-phase overhead transmission line.
The parameters computed are the resistance R, reactance X, susceptance B, and conductance G. These values are computed as distributed (per unit of distance), lumped or total (for a specific line distance), and in per-unit.
Calculations
The following controls are part of the calculations section:
Parameters Calculation
This section is to enter the necessary data to compute the characteristic line parameters that are shown in the Results panel.
Input Data
Conductor Type: This is the combo box that lists all the conductor types available in the Conductors table. To add, remove or edit a specific conductor and its characteristics, see Conductor Type section below.
Tower Configuration: This combo box lists all the tower configurations available in the Tower Configurations table. To add, remove or edit a specific tower configuration, please go to the Tower Configuration section below.
Line Length: This is the value of the distance of the transmission line. The units are miles when using English system, or kilometers when using the Metric (SI) system.
Line Length Units: The line length units specify the measurement system to use when entering the line length. The options are English system or Metric (SI) system. The final and intermediate results will also be shown in the system specified here.
Power Base: The system voltampere base in MVA.
Voltage Base: The line-line voltage base in KV.
Impedance Base: The impedance base in Ohms. This value is automatically computed when the power base and the voltage base are entered or modified.
Admittance Base: The admittance base in Siemens. It is also automatically computed as the inverse of the impedance base.
Final Results
When all the input data is entered, the results automatically will be displayed. The values for R, X, B and G are shown in three different sections, each section corresponding to Distributed, Lumped or Total, and Per Unit values, respectively. The Power Surge Impedance Loading is calculated only for the lumped section.
Intermediate Results
The intermediate values calculated to compute the R, X, B, and G values are displayed here. The computed geometric mean radius and geometric mean distance are shown in the Distributed values section. The characteristic impedance and propagation factor are displayed in the Lumped values section.
Note: To see the specific calculations used in this program, see the Calculations section, at the end of this document.
Ampere to MVA Limit Conversion
This section converts the limits of the transmission line from Amperes to MVAs, given the voltage base, and vice versa.
Conductor Type
This section is used to add, remove, rename, and edit the information related to the conductor types. This can be done in two ways: using the form for an individual conductor type, or using the table for all the conductor types available.
Edit By Form
Conductors are identified by a unique code word. All the available conductors are listed in the Conductor Code Word combo box. By selecting one conductor, all its properties are displayed in the form. There, the user is able to modify any of those values. After modification of any value, the user has to save the changes by clicking on the button Save before changing tabs, otherwise the changes will be lost.
By clicking on New, a message prompting for a name for a new conductor will be shown. By clicking on Rename, a new name for the current conductor type is required. In order to save the current conductor type with a different name is necessary to click on Save As. Finally, to remove the current conductor the user can do so by clicking on the Delete button.
Edit By Table
In this tab, all the conductor types are shown as records in a table, where every field is a characteristic of the conductor. In order to edit the records in this table, use the Database button described in the Database section. While editing the table, the user can not change of tab until changes are posted or discarded.
Conductor Properties
The available properties of the conductors are the following:
Code Word: Code name for the type of conductor. The names of bird species are typically used. Code Word has to be unique.
Area: The area of aluminum conductor in circular mils. A circular mil is the cross-sectional area of a circular conductor having a diameter of 1 mil. One mil is one thousandth of an inch (0.001").
Aluminum strands: Number of aluminum strands.
Steel layers: Number of steel strands.
Aluminum layers: Number of aluminum layers.
External diameter: Outside diameter of the conductor in inches.
GMR: Geometric Mean Radius in feet.
DC Resistance: DC resistance of the conductor at 20°C per 1 mile in Ohms.
AC Resistance 25: AC resistance of the conductor at 60 Hz and 25°C per 1 mile in Ohms.
AC Resistance 50: AC resistance of the conductor at 60 Hz and 50°C per 1 mile in Ohms.
AC Resistance 75: AC resistance of the conductor at 60 Hz and 75°C per 1 mile in Ohms.
Inductive Reactance: Inductive reactance per conductor at 1 foot spacing at 60 Hz in Ohms/mile.
Capacitive Reactance: Capacitive reactance per conductor at 1 foot spacing at 60 Hz in MegaOhms/mile.
Tower Configuration
This part is used to add, remove, rename, and edit the information related to the tower configurations. This can be done in two ways: using the form for an individual tower configuration, or using the table for all the tower configurations available.
Edit By Form
Tower configurations are identified by a unique name. All the available tower configurations are listed in the Tower Configuration Name combo box. By selecting one specific tower configuration, all its characteristics are displayed in the form. There, the user can modify any of those characteristics. After modification of any value, the user has to save the changes by clicking on the button Save before changing tabs, otherwise the changes will be lost.
By clicking on New, a message prompting for a name for a new tower configuration will be shown. By clicking on Rename, a new name for the current tower configuration is required. In order to save the current tower configuration with a different name is necessary to click on Save As. Finally, to remove the current tower configuration the user can do so by clicking on the Delete button.
Edit By Table
In this tab, all the tower configurations are shown as records in a table, where every field is a value of the tower configuration. In order to edit the records in this table, use the Database button described in the Database section. While editing the table, the user can not change of tab until changes are posted or discarded.
Tower Configuration Values
The values of the tower configuration are the following:
Name: Name for the tower configuration. Name has to be unique.
Phase spacing: x and y coordinates of phases A, B and C positions. Values are in feet for English system and meters for Metric (SI) system. When these values are modified, the phase spacing graph is automatically updated. Draw axis has to be checked for x and y axis to be drawn in the graph.
Conductors per bundle: This section specifies the number of conductors (either single conductor or a bundle of conductors) per phase. The maximum number of conductors per bundle allowed is 4.
Use regular spacing: When using a bundle of conductors, checking the Use Regular Spacing of check box will use the specified value as a regular spacing among the conductors. If the Use Regular Spacing of check box is not checked, then the custom conductors spacing section has to be used.
Conductors spacing: x and y coordinates of the conductors in the bundle. Values are in feet for English system and meters for Metric (SI) system. When these values are modified, the bundle spacing graph is automatically updated. Draw axis has to be checked for x and y axis to be drawn in the graph.
Temperature: Assumed temperature in Fahrenheit degrees for English system and Celsius degrees for Metric (SI) system.
Frequency: Frequency of the system in Hertz.
System of units: The system of units used to specify the values of the tower configuration. The options are English system or Metric (SI) system. The units specified here not necessarily have to math the units specified in the Input Data section.
Database
The conductor type and tower configurations tables are read by default from the file conductors.mbd, which is a MS Access® database. This database can be read from another *.mdb file by clicking on the Select Conductors and Configurations Database button.
Note: The conductors.mdb file can also be viewed and edited in MS Access®.
In order to edit a record in the database tables, the user can use the toolbar designed to do that. Following there is a figure showing this toolbar:
The First, Prior, Next, and Last buttons are used to move among records. The Insert, Delete and Edit buttons are used to insert, delete or edit the current record, respectively. While editing a record, the user can not change of tab until modifications are posted through the Post edit button or canceled with the Cancel edit button. The Refresh data button just refreshed the data of the entire table.
Calculations
Distributed Parameters
Resistance
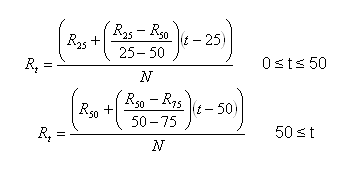
Where:
Rt AC resistance at temperature t per phase per 1 mile in Ohms
t Assumed temperature in Celsius degrees
R25 AC resistance of the conductor at 60 Hz and 25°C per 1 mile in Ohms
R50 AC resistance of the conductor at 60 Hz and 50°C per 1 mile in Ohms
R75 AC resistance of the conductor at 60 Hz and 75°C per 1 mile in Ohms
N Number of conductors per phase
Inductive Reactance
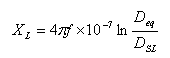
Where:
XL Inductive reactance in Ohms/meter
f Frequency of the system in Hertz
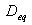 Geometric mean distance between phases in meters
Geometric mean distance between phases in meters
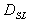 Geometric mean radius between conductors of one phase in meters
Geometric mean radius between conductors of one phase in meters
The geometric mean distance between phases is defined as:
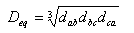
Where:
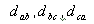 Distances between phases a-b, b-c, c-a, respectively in meters
Distances between phases a-b, b-c, c-a, respectively in meters
The geometric mean radius between conductors of one phase is defined as:
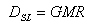 For 1 stranded conductor
For 1 stranded conductor
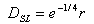 For 1 solid cylindrical conductor
For 1 solid cylindrical conductor
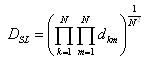 For more then 1 conductor bundle
For more then 1 conductor bundle
Where:
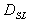 Geometric mean radius in meters
Geometric mean radius in meters
r External radius of conductor in meters
GMR Geometric mean radius given in tables for one stranded conductor
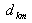 Distance between conductors k and m in meters.
Distance between conductors k and m in meters.
Note: If k = m, then 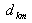 =
= 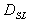 for one stranded or solid cylindrical conductor.
for one stranded or solid cylindrical conductor.
Susceptance
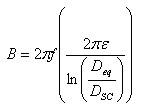
Where:
B Susceptance in Siemens/meter
f Frequency of the system in Hertz
e Constant permittivity = 8.85418 ´ 10-12
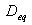 Geometric mean distance between phases, defined as above
Geometric mean distance between phases, defined as above
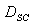 Geometric mean radius between conductors of one phase using external radius in meters
Geometric mean radius between conductors of one phase using external radius in meters
The geometric mean radius between conductors of one phase using external radius is defined as:
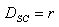 For 1 conductor
For 1 conductor
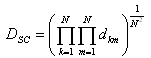 For more then 1 conductor bundle
For more then 1 conductor bundle
Where:
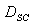 Geometric mean radius in meters
Geometric mean radius in meters
r External radius of conductor in meters
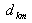 Distance between conductors k and m in meters.
Distance between conductors k and m in meters.
Note: If k = m, then 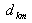 = r.
= r.
Conductance
Assumed G = 0
Where:
G Conductance in Siemens/meter
Lumped (Total) Parameters
Resistance, Inductive Reactance, Conductance and Susceptance, using the equivalent p circuit (long line)
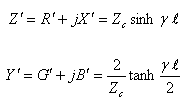
Where:
Z’ Total series impedance of line in Ohms
Y’ Total series admittance of line in Siemens
R’ Total series resistance of line in Ohms
X’ Total series inductive reactance of line in Ohms
G’ Total series conductance of line in Siemens
B’ Total series susceptance of line in Siemens
Zc Characteristic impedance in Ohms
g Propagation constant in meters-1
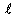 Line length in meters
Line length in meters
The characteristic impedance and propagation constant are defined as:
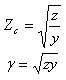
Where:
z Distributed series impedance in Ohms/meter
y Distributed series admittance in Siemens/meter
The distributed series impedance and distributed series admittance are defined as:
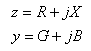
Where:
R Distributed series resistance in Ohms/meter
X Distributed series inductive reactance in Ohms/meter
G Distributed series conductance in Siemens/meter
B Distributed series susceptance in Siemens/meter
Surge Impedance Loading
The surge impedance loading is defined as the power delivered by a lossless line to a load resistance equal to the surge (or characteristic) impedance Zc, and is given by:
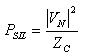
Where:
PSIL Total surge impedance loading in a three-phase line in VA
VN Line-line nominal voltage in Volts
Base Values
Impedance Base
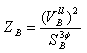
Where:
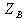 Impedance base in Ohms
Impedance base in Ohms
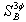 Power base in VA
Power base in VA
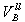 Line-line voltage base in Volts
Line-line voltage base in Volts
Admittance Base
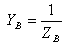
Where:
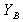 Admittance base in Siemens
Admittance base in Siemens
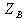 Impedance base in Ohms
Impedance base in Ohms
Per Unit (PU) Parameters
Resistance, Inductive Reactance, Conductance, Susceptance
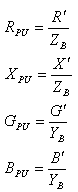
Where:
RPU Per unit resistance
R’ Total series resistance in Ohms
XPU Per unit Inductive reactance
X’ Total series inductive reactance in Ohms
XPU Per unit conductance
G’ Total series conductance in Siemens
BPU Per unit susceptance
B’ Total series susceptance in Siemens
ZB Impedance base in Ohms
YB Admittance base in Siemens
MVA To Ampere and Ampere To MVA Limits Conversion
MVA to Ampere Limit Conversion
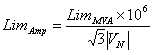
Where:
LimAmp Limit in Amperes
LimMVA Limit in MVAs
VN Nominal voltage in Volts
Ampere to MVA Limit Conversion
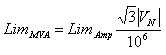
Where:
LimAmp Limit in Amperes
LimMVA Limit in MVAs
VN Nominal voltage in Volts