Limit Monitoring Settings and Limit Violations Dialog
The Limit Monitoring Settings Dialog is accessed from several locations.
Limit Monitoring Settings button on either the Case Information ribbon tab
Limit Monitoring Settings button on the Other Tools Ribbon Group of the Tools ribbon tab.
Many different tool dialogs such as the Contingency Analysis Dialog and Available Transfer Capability Dialog,
The Limit Monitoring Settings Dialog gives you ability to specify which limits you want to monitor, and thus enforce in the various tools that Simulator provides. In general, keep in mind that a bus, transmission line/transformer, or interface’s limit is monitored only if the following conditions are met.
Conditions for Monitoring an Element’s Limit
- Its Monitor field is set to YES
- Its Limit Group is Enabled
- Its Area is set to Report Limits and it meets the KV range for reporting
- Its Zone is set to Report Limits and it meets the KV range for reporting
The following fields are shown on the display:
Elements To Show
Change this value to modify which elements are displayed in the Buses, Lines, and Interfaces. Set it to…
All Elements to show all Buses, Lines and Interfaces regardless of monitoring settings.
Monitored Elements to only display Buses, Lines and Interfaces that meet the conditions for monitoring. See Limit Monitoring Settings for more information on setting which values are monitored.
Violating Elements to only display Buses, Lines and Interfaces that are violating. See Limit Monitoring Settings for more information on setting what is considered a violation.
Number of Violations
The following fields provide summary information on the types of violations that are currently present in the case:
High Voltage Buses and Low Voltage Buses
Shows the total number of bus voltage magnitude violations. These violations are shown on the Bus Voltage Magnitude Limit Violations Display.
Low Voltage Suspects
Shows the total number of buses whose voltages have fallen below a designated internal threshold to indicate a low voltage solution is being reached in some location in the system.
Line/Transformer Violations
Shows the total number of line/transformer violations. These violations are shown on Line and Transformer Limit Display.
Interface Violations
Indicates the total number of interface violations. These violations are shown on the Interface Violations Display.
Bus Pair ViolationsAdded in Version 20
Indicates the total number of bus pair violations. These violations are shown on the Bus Pair Violations Display.
Limit Group Values
This part of the dialog shows information about the Limit Groups with greater description shown below.
Save/Load Monitoring Settings
The Save and Load Monitoring Settings buttons allow the user to save the current set or load a previously saved set of Limit Monitoring Settings options. The options are saved in a PowerWorld Auxiliary File text format.
Do not monitor radial lines and buses
Check this box to ignore limits on radial lines and buses throughout the case. In this instance a radial bus is defined as a bus that is connected to the rest of the power system by a single in-service transmission line. A radial line is the defined as a line connected to a radial bus. This means that in a 5 lines in series that connect to a radial load, only the last bus and last line will be considered radial.
If you would like to better determine which lines are "radial" in a more traditional sense, use the feature Branches that Create Islands that allows you to easily generate a list of branches that if taken out of service will split an existing island into two. These represent lines which may be considered radial.
Radial lines and buses are always monitored when using the Integrated Topology Processing add-on, and this option is ignored.
Tabs on the Limit Monitoring Dialog
The tabs on the Limit Monitoring Settings Dialog allow you to change these settings. These tabs contain tables showing lists of the respective elements. Since these tables are another variety of the Case Information Displays, you may interact with it in a familiar manner. Click on any of the field headings to sort by that field. Right-click on the display to call up the display’s local menu. From the local menu, you can print the violations, copy the violation records to the Windows clipboard for use with another application, modify the format and content of the violations listing, view the information dialog of the respective element, and view the Quick Power Flow List or Bus View Display.
Buses Tab
Each tab shows a list of the respective type of power system element. The important columns include:
Number, Name:Bus number between 1 and 99,999, and its alphanumeric identifier.
Area Name:Alphanumeric identifier of the bus’ area.
Monitor: toggle this between YES and NO to set whether the specific element should be monitored.
Limit Group: toggle this value to specify which Limit Group the element belongs to
PU Volt:Bus’ per unit voltage magnitude.
Volt (kV): Bus’ actual voltage magnitude in kV. This is the per unit voltage magnitude multiplied by the bus’ nominal voltage.
Limit Low PU Volt: Bus' individual low voltage limit used when the bus is set to use specific voltage limits other than the default voltage limit defined in the bus' limit group. This field is not enabled unless the "Use Specific Limits" option for the bus is set to YES. The value will then reflect the low per unit voltage limit specified in one of the eight low voltage limit sets that can be defined with the bus. Which voltage limit set's value is displayed depends on which limit set is specified as the "Bus Low Rate Set" in the limit group to which the bus is assigned.
Limit High PU Volt: Bus' individual high voltage limit used when the bus is set to use specific voltage limits other than the default voltage limit defined in the bus' limit group. This field is not enabled unless the "Use Specific Limits" option for the bus is set to YES. The value will then reflect the high per unit voltage limit specified in one of the eight high voltage limit sets that can be defined with the bus. Which voltage limit set's value is displayed depends on which limit set is specified as the "Bus High Rate Set" in the limit group to which the bus is assigned.
Contingency Limit Low PU Volt: Bus' individual low voltage limit used during a contingency when the bus is set to use specific voltage limits other than the default voltage limit defined in the bus' limit group. This field is not enabled unless the "Use Specific Limits" option for the bus is set to YES. The value will then reflect the contingency low per unit voltage limit specified in one of the eight contingency low voltage limit sets that can be defined with the bus. Which contingency voltage limit set's value is displayed depends on which limit set is specified as the "Bus CTG Low Rate Set" in the limit group to which the bus is assigned.
Contingency Limit High PU Volt: Bus' individual high voltage limit used during a contingency when the bus is set to use specific voltage limits other than the default voltage limit defined in the bus' limit group. This field is not enabled unless the "Use Specific Limits" option for the bus is set to YES. The value will then reflect the contingency high per unit voltage limit specified in one of the eight contingency high voltage limit sets that can be defined with the bus. Which contingency voltage limit set's value is displayed depends on which limit set is specified as the "Bus CTG High Rate Set" in the limit group to which the bus is assigned.
Note: If Elements to Show is set to Monitored Elements, then only elements which meet the conditions for monitoring will be displayed in these lists.
If using the Integrated Topology Processing add-on, the Only show the primary bus for each superbus checkbox will be available. Checking this box will limit the buses shown to only those that are primary buses. This provides a quick means of removing the clutter of redundant data. The primary buses and superbuses are determined from the base case topology. In addition to monitoring the primary bus for each superbus, the bus with the highest low voltage limit and the bus with the lowest high voltage limit will also be monitored so as not to miss any possible violations.
Lines Tab
Each tab shows a list of the respective type of power system element. The important columns include
From Bus Number and Name:Bus number at name at the from terminal of the line. For transformers, the from bus is the tapped side. Right- clicking on either of these fields allows you to see all the flows measured at the "from" bus using the Quick Power Flow List or Bus View Display local menu options.
To Bus Number and Name:Bus number at name at the to terminal of the line. For transformers, the to bus is the untapped side. Right-clicking on either of these fields allows you to see all the flows into the "to" bus using the Quick Power Flow List or Bus View Display local menu options.
Circuit:Two-character identifier used to distinguish between multiple lines joining the same two buses.
Monitor: toggle this between YES and NO to set whether the specific element should be monitored.
Limit Group: toggle this value to specify which Limit Groups the element belongs to
Used Limiting Flow, Limit, Used % of Limit:The flow at the end of the branch selected for measurement, and its MVA or Amp limit. The percentage equivalent of the flow to it’s limit is given in the Used % of Limit column.
MVA or Amps?: Units used with the Max Flow and the Limit field. All flows are expressed either in MVA or amps.
Note: If Elements to Show is set to Monitored Elements, then only elements which meet the conditions for monitoring will be displayed in these lists.
Interfaces, Bus Pairs, and Nomograms Tab
Similar to the Buses and Lines Tabs shown above. The important columns are the Monitor and Limit Group columns
Area Reporting and Zone Reporting Tabs
These tabs display all the Areas and Zones in the system. The important columns are
Report Limits:toggle this between YES and NO to set whether the specific element should be monitored.
Report Min kV and Report Max kV:Only buses and lines within this kV range will be monitored.
Modify/Create Limit Group Tab
Every power system elements belongs to a single Limit Group. By default, all power system elements are in the same Limit Group that is named "Default". New limit groups can be added by right-clicking in the table and choosing Insert from the popup menu. Additional limit groups give the flexibility of assigning devices to different groups, where each group can have its own set of defined limit information.
The limit group stores important values regarding the enforcement and monitoring of the power system elements within the Limit Group. The values are:
Disabled: Set the value to YES to ignore all power system element limits in the Limit Group. Set the value to NO to monitor limits according to the settings of the Limit Group.
Branch Percentage: The percentage to which Simulator’s study tools will limit a line or transformer. Typically this is 100%, but it can be modified. In Contingency Analysis, then lines will be flagged as violated if they exceed this percentage. In performing an Optimal Power Flow, all attempts will be made to keep the line below this percentage.
Line Rate Set: You may define eight different ratings to transmission lines or transformers (for more information see Line/Transformer Information). Change this value to specify which rating set should be used for lines/transformers in the limit group.
Contingency Line Rate Set: This field specifies the rating set used for post-contingency monitoring of Lines/Transformers.
Amps or MVA: Limits for transmission lines and transformers are always entered in MVA. However, when reporting limit violations, it is common to check transmission line limits in terms of their amp loading. If the Treat Line Limits As Equivalent Amps is checked, the limits for transmission lines are reported in amps rather than MVA. If this box is not checked, limits for both transmission lines and transformers are expressed in MVA.
For reference, note that the amp rating of a line is derived from the MVA rating using the formula
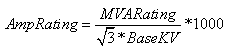
Also note that the reported Amp% and MVA% will be different by a factor of the per unit voltage at the bus terminal at which the limiting flow is determined. This is often a point of confusion as the expectation might be that the percent loading would be the same regardless of which reporting method is used: Amp% = MVA%/(Per Unit Voltage)
When doing contingency analysis and the Power Flow Solution Options are set to Use the DC Approximation in Power Flow, this option will be ignored. Line limits will always be reported in MVA when using the DC approximation.
Interface Percentage: The percentage to which Simulator’s study tools will limit an interface. Typically this is 100%, but it can be modified. In Contingency Analysis, then interfaces will be flagged as violated if they exceed this percentage. In performing an Optimal Power Flow, all attempts will be made to keep the interface below this percentage.
Interface Rate Set: You may define 15 different ratings to an interface. Change this value to specify which rating set should be used for interfaces in the limit group.
Interface Contingency Rate Set: This field specifies the rating set used for post-contingency monitoring of Interfaces during Contingency Analysis.
Bus Pair Percentage:Added in Version 20 The percentage to which Simulator’s study tools will limit an bus pair. Typically this is 100%, but it can be modified. In Contingency Analysis, then bus pairs will be flagged as violated if they exceed this percentage of their limit..
Bus Pair Rate Set: Added in Version 20You may define 4 different ratings to an bus pair. Change this value to specify which rating set should be used for bus pair in the limit group.
Bus Pair Contingency Rate Set:Added in Version 20 This field specifies the rating set used for post-contingency monitoring of bus pairs during Contingency Analysis.
Low PU Volt: Buses will be flagged as violated if they fall below this per unit voltage.
High PU Volt: Buses will be flagged as violated if they go above this per unit voltage.
Contingency Low PU Volt: Buses will be flagged as violated during contingencies if they fall below this per unit voltage.
Contingency High PU Volt: Buses will be flagged as violated during contingencies if they go above this per unit voltage.
Bus Low Rate Set: This field value indicates which bus voltage rating set should be used for normal (non-contingency) low voltage violation reporting.
Bus High Rate Set: This field value indicates which bus voltage rating set should be used for normal (non-contingency) high voltage violation reporting.
Bus Contingency Low Rate Set: This field value indicates which bus voltage rating set should be used for low voltage contingency violation reporting.
Bus Contingency High Rate Set: This field value indicates which bus voltage rating set should be used for high voltage contingency violation reporting.
Nomogram Percentage: The percentage to which Simulator’s study tools will limit a nomogram.
Limiting End: Specified as higher or lower, this field determines whether the higher or the lower flow amount on the element is used for reporting a limit violation. If you use higher, it is possible that the lower flow is not violating the line limit. If you use lower, then you are guaranteed that the element limit is being violated at both ends of the element.
Use Limit Cost: If this field is set to yes, you are enabling the capability to have a cost function associated with enforcing constraints. This cost function can be viewed as similar to a generator cost function, in that as the constraint becomes overloaded by larger amounts, the marginal cost of enforcing the constraint will increase. For setting the piecewise linear limit cost curve, right-click and choose show dialog from the popup menu to access the Limit Group Dialog.
Often monitoring elements according to Area and/or Zone is all that you need. However, if you need to monitor specific groups of power system elements and not others then you need to create some new Limit Groups.